I. Introduction
In the world of modern construction, the pursuit of efficiency, sustainability, and cost-effectiveness has driven the development of various innovative technologies. One such advancement is the Bubble Deck Slab, a type of hollow, flat slab designed to enhance structural performance while reducing material usage and weight. Originally developed by Jorgen Bruenig in the 1990s in Denmark, the Bubble Deck Slab has seen increasing application in industrial projects globally. This article delves into the features, types, materials, installation process, advantages, and applicability of the Bubble Deck Slab.
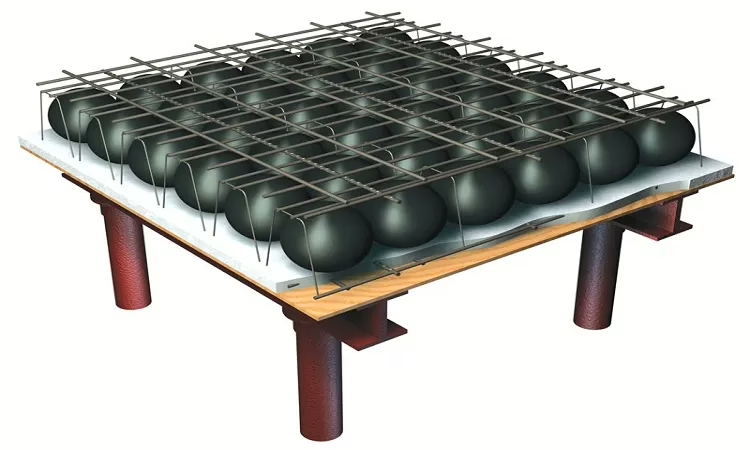
II. Basic Principle of Bubble Deck Slab
At its core, the Bubble Deck Slab is a revolutionary concept that replaces a significant portion of the concrete in traditional floor slabs with hollow plastic spheres. These spheres, which do not contribute to the slab’s structural strength, are strategically placed in the middle of the slab, reducing the overall weight. The principle behind the Bubble Deck Slab is simple yet effective—by eliminating the non-structural concrete in the center, the slab becomes significantly lighter while maintaining its load-bearing capacity. This reduction in weight not only saves on materials but also reduces the structural load on buildings, making construction more efficient.
III. Types of Bubble Deck Slab
The Bubble Deck Slab comes in three primary types, each suited for different construction needs.
- Type A – Filigree Elements Type A is a hybrid solution that combines precast and unassembled elements. It includes a 60mm thick concrete layer with steel reinforcement and bubbles that remain unattached. On-site, the bubbles are supported by temporary stands, and the entire structure is held in place by interconnected steel mesh. This type is particularly advantageous in new construction projects where designers can customize bubble placement and reinforcement layout according to the building’s specifications.
- Type B – Reinforcement Modules Type B consists of pre-assembled modules that include steel mesh and plastic bubbles. These components are transported to the site and placed on traditional formwork. Once in position, they are connected with additional reinforcement and then concreted using traditional methods. Type B is ideal for projects with limited space since the modules can be stacked for storage before installation.
- Type C – Finished Planks Type C is the most complete form of Bubble Deck Slab. These are factory-made planks that include plastic spheres, reinforcement mesh, and concrete, delivered in their finished form. Unlike Types A and B, Type C is designed for shorter spans and one-way applications, typically used in situations where there is a limited construction schedule.
IV. Material Specifications Used in Bubble Deck Slab
The materials used in the construction of Bubble Deck Slabs are key to their performance and efficiency.
- Concrete Concrete used in Bubble Deck slabs must meet a minimum grade of M20-25, particularly for joint filling. Self-compacting concrete is often used due to its ability to flow around tight reinforcement spaces, ensuring proper filling without air pockets. This type of concrete helps ensure high quality and uniformity during construction.
- Reinforcement Bars The reinforcement in Bubble Deck slabs consists of two meshes, one placed at the top and one at the bottom. The steel used for reinforcement is fabricated in two forms: meshed layers for lateral support and diagonal girders for vertical support of the bubbles. Steel reinforcement typically utilizes Fe-500 grade or higher, ensuring strength and stability.
- Hollow Bubbles The plastic spheres incorporated in Bubble Deck slabs are made from high-density polypropylene, a material that is chemically inert and non-reactive with concrete and reinforcement bars. The size and spacing of the bubbles vary, with diameters ranging from 180mm to 360mm. These bubbles can be spherical or ellipsoidal and are designed to support depths of up to 450mm, allowing for slabs with varying thicknesses.
V. Installation of Bubble Deck Slab
The installation process of the Bubble Deck Slab is relatively straightforward, involving several key steps to ensure efficiency and structural integrity.
- Element Division The overall floor area is divided into individual elements, typically up to 3 meters wide, depending on site access.
- Reinforcement Setup These elements consist of pre-assembled top and bottom reinforcement meshes, joined together by vertical lattice girders. The plastic void formers (bubbles) are placed between the mesh layers, forming what is known as a “bubble-reinforcement sandwich.”
- Pre-Cast Concrete Layer A 60mm pre-cast concrete layer is cast around the bottom mesh, creating permanent formwork for part of the slab depth.
- Assembly on-site On-site, the individual elements are “stitched” together with loose reinforcement placed across the joints between the elements. Once the site is prepared, concrete is poured and cured, completing the slab.
The result is a seamless biaxial floor slab that integrates all components into a single, cohesive structure.
VI. Advantages of Bubble Deck Slab
The adoption of Bubble Deck Slab brings a host of advantages to modern construction, including:
- Superior Statics The reduction in weight, coupled with increased strength, means fewer columns and the elimination of beams or ribs under ceilings, offering greater design flexibility.
- Production and Execution Bubble Deck slabs are prefabricated, ensuring higher quality control and reducing on-site construction errors. Their lightweight nature also simplifies installation with minimal need for heavy lifting equipment.
- Transportation Due to the reduced material weight, transportation costs are lower, contributing to overall cost savings and reduced environmental impact.
- Economic Savings Significant savings are realized in both materials and transportation costs. The lightweight nature of Bubble Deck slabs allows for savings of up to 50% in materials such as slabs, pillars, and foundations.
- Safety Bubble Deck slabs are fireproof and offer improved earthquake resistance, adding an additional layer of safety to buildings.
- Environmental Improvement By replacing heavy concrete with plastic spheres, the energy consumption during production, transportation, and construction is reduced. This leads to a notable decrease in CO2 emissions, making Bubble Deck slabs an environmentally friendly alternative.
- Explosion Safety The biaxial flat slab system is ideal for structures that require high resistance to explosions, effectively reducing the risk of collapse in the event of a blast.
VII. Functional Applicability of Bubble Deck Slab
The versatility of Bubble Deck Slabs makes them applicable in a wide range of construction projects. These slabs are used in residential buildings, offices, industrial facilities, schools, hospitals, and more. They are particularly well-suited for large-scale developments, such as apartments, villas, hotels, and parking garages, due to their efficiency, strength, and sustainability.
VIII. Case Study: Millennium Tower
One of the most notable examples of the use of Bubble Deck Slabs is the Millennium Tower in Holland, which was one of the first major structures to incorporate this technology. The successful implementation of the Bubble Deck system in such a high-profile project demonstrated its effectiveness and paved the way for its broader adoption in the construction industry.
IX. Conclusion
The Bubble Deck Slab represents a significant leap forward in construction technology, offering numerous advantages over traditional slab systems. Its lightweight design, coupled with enhanced strength, energy efficiency, and safety, makes it an ideal choice for a wide range of construction projects. As the demand for sustainable and cost-effective building solutions continues to grow, the Bubble Deck Slab is likely to play a key role in shaping the future of the construction industry.
