The design and construction of foundations play a crucial role in the overall cost and durability of a structure. Economical foundations not only reduce initial construction expenses but also prevent potential structural issues in the future. Addressing practical construction problems during the design phase ensures efficiency, reliability, and cost-effectiveness.
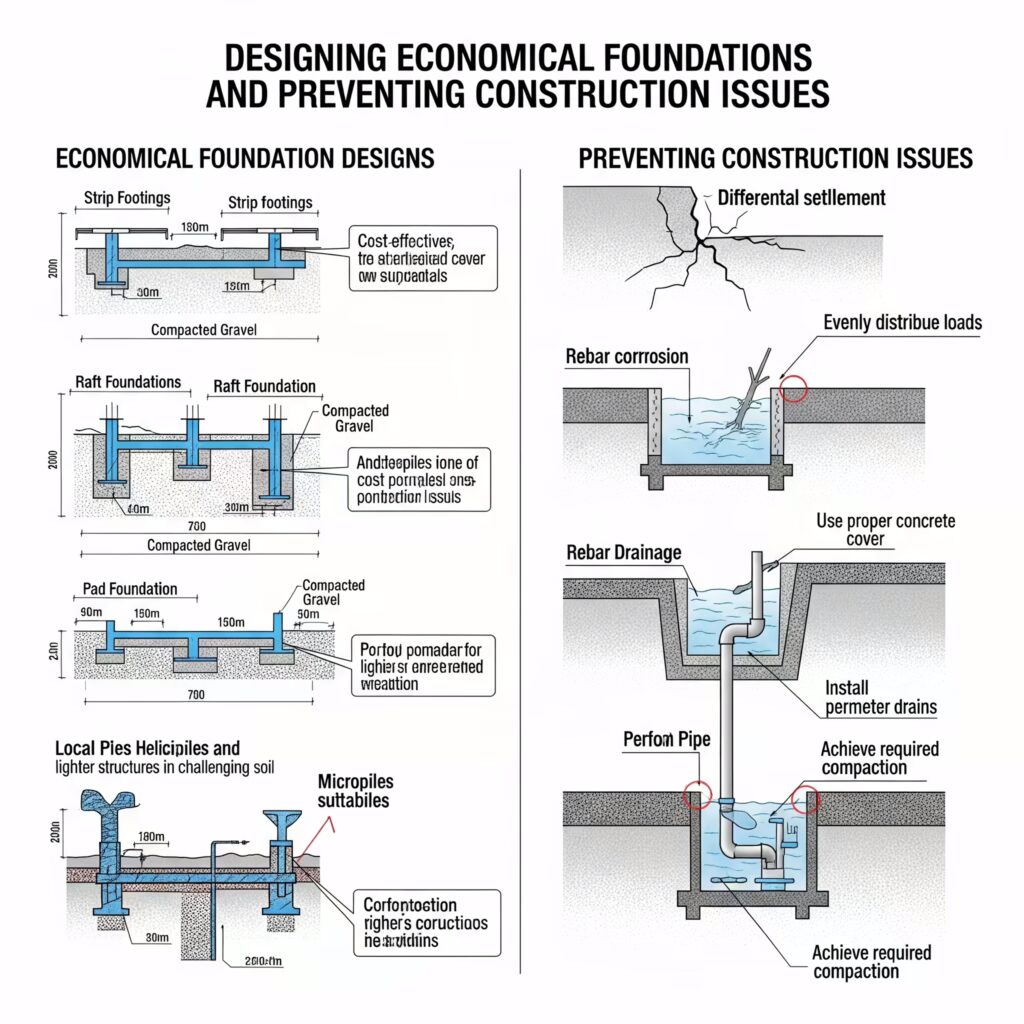
Key Considerations for Economical Foundation Design
To achieve cost efficiency and minimize potential problems, foundation design must consider several factors, including ground conditions, construction methods, and material choices. Proper planning ensures that the foundation remains stable while optimizing costs.
Practical Construction Problems and Cost Factors
3.1 Make the Foundation Shallow for Economy
One of the primary ways to reduce foundation costs is by keeping it as shallow as possible. A foundation should be designed to sufficiently support the structure while avoiding excessive depth and width. This approach is particularly important when constructing on saturated soil, where deeper foundations significantly increase costs due to additional stabilization and water management requirements.
3.2 Reduce Cost of Foundation Construction
Cost reduction can be achieved through the continuous evaluation of construction techniques and standards. Outdated construction practices often lead to unnecessary expenses. Adopting modern, efficient methods and using locally available materials can contribute to a more economical foundation.
3.3 Awareness of Structural Designer
A structural designer must be well-informed about the ground conditions and practical aspects of construction. Assumptions made during the design phase should align with real-site conditions. A well-prepared designer can ensure a cost-effective foundation that minimizes the risk of construction delays and unforeseen complications.
3.4 Prevent the Use of Expensive and Complex Formworks
Formworks contribute significantly to foundation construction costs. Designers should aim for simplicity by minimizing the need for complex or costly formwork systems. For instance, site inspections can be performed using trial pits instead of deep excavations, reducing time and labor expenses.
3.5 Reliability of Site Investigation
The accuracy of a site investigation report is crucial to ensuring a well-planned foundation. Poorly conducted soil investigations can lead to unforeseen foundation issues, resulting in higher costs. Proper site exploration must be conducted to prevent delays and additional expenses during construction.
3.6 Decision Between Fast or Slow Foundation Construction
The speed of foundation construction can impact costs. While slow construction may seem cost-effective in some cases, fast-tracked construction is sometimes the more economical choice, especially in saturated soil conditions. Prolonged dewatering processes can increase expenses, making an accelerated construction process more viable.
3.7 Effect of Foundation Construction on Surrounding Structures
Foundation construction can affect nearby buildings and infrastructure. Excavation, compaction activities, and machine vibrations can lead to structural damage in adjacent properties. Designers should assess and mitigate these risks to ensure the stability of surrounding structures.
3.8 Variations in Foundation Geometry and Joint Requirements
Changes in foundation design, such as variations in shape and rigidity, must be carefully planned. Proper joints should be incorporated to accommodate movement and settlement, ensuring the long-term stability of the foundation.
3.9 Impact of Undesired Factors on Constructed Foundations
Several external factors can affect a foundation after construction. These include:
- Ground movement due to shrinkage or frost heave
- Influence of tree roots on soil stability
- Sulfate attack on concrete foundations
- Construction of new structures in proximity, leading to additional stress
Designers must consider these factors during the design phase to ensure the durability of the foundation.
Conclusion
A well-designed foundation balances cost, safety, and long-term durability. By optimizing design choices, minimizing unnecessary expenses, and considering practical construction challenges, engineers can create economical foundations that stand the test of time. Proper planning and site assessment ensure not only a cost-effective construction process but also a structure that remains stable and resilient for years to come.
